在C# .NET中,Func、Predicate和Expression是三種常用的委托和表達式類型,它們在編寫靈活、可重用的代碼時非常有用。本文將詳細介紹這三種類型,并提供多個實例來說明它們的用法和區別。
1. Func<T, TResult>
Func是一個通用委托,它可以接受零個或多個輸入參數,并返回一個值。其基本形式為:
public delegate TResult Func<out TResult>();public delegate TResult Func<in T, out TResult>(T arg);public delegate TResult Func<in T1, in T2, out TResult>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2);// ... 最多可以有16個輸入參數
示例1:基本用法
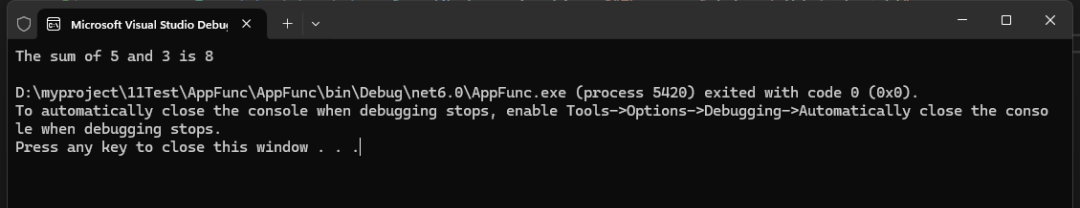
Func<int, int, string> formatNumber = (a, b) => $"The sum of {a} and {b} is {a + b}";string result = formatNumber(5, 3);Console.WriteLine(result);
示例2:作為方法參數
public static List<int> FilterList(List<int> numbers, Func<int, bool> filterFunc){ return numbers.Where(filterFunc).ToList();}
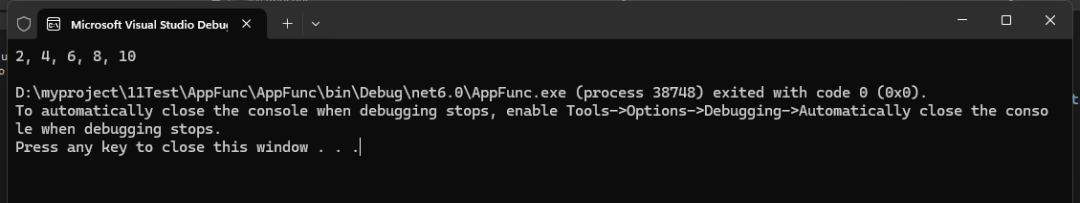
static void Main(string[] args){ // 使用 List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }; List<int> evenNumbers = FilterList(numbers, n => n % 2 == 0); Console.WriteLine(string.Join(", ", evenNumbers));}
2. Predicate<T>
Predicate是一個特殊的Func,它始終返回一個布爾值。它通常用于定義過濾條件。
public delegate bool Predicate<in T>(T obj);
示例3:使用Predicate
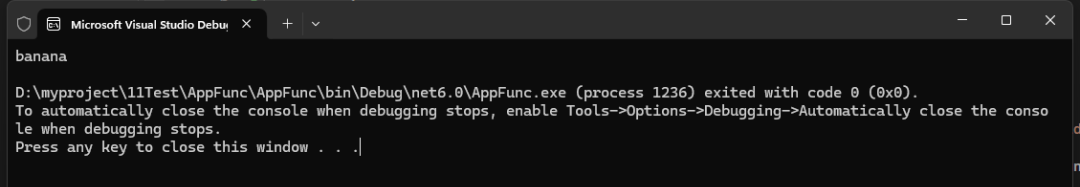
static void Main(string[] args){ List<string> fruits = new List<string> { "apple", "banana", "cherry", "date", "elderberry" };
Predicate<string> startsWithB = s => s.StartsWith("b", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase); string bFruit = fruits.Find(startsWithB);
Console.WriteLine(bFruit);}
示例4:Predicate vs Func
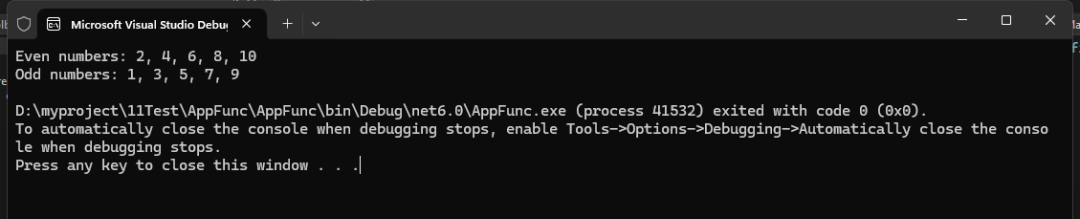
static void Main(string[] args){ // 使用Predicate Predicate<int> isEven = n => n % 2 == 0; List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }; List<int> evenNumbers = numbers.FindAll(isEven);
// 使用Func Func<int, bool> isOdd = n => n % 2 != 0; List<int> oddNumbers = numbers.Where(isOdd).ToList();
Console.WriteLine($"Even numbers: {string.Join(", ", evenNumbers)}"); Console.WriteLine($"Odd numbers: {string.Join(", ", oddNumbers)}");}
3. Expression<T>
Expression表示一個可以編譯和執行的代碼塊。它們通常用于構建動態查詢、規則引擎或者在運行時修改代碼行為。
示例5:基本Expression
static void Main(string[] args){ Expression<Func<int, bool>> isPositive = n => n > 0;
// 編譯并執行Expression Func<int, bool> compiledFunc = isPositive.Compile(); bool result = compiledFunc(5); Console.WriteLine(result);}
示例6:構建動態查詢
public class Person{ public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; }}
public static Expression<Func<Person, bool>> BuildAgeRangeExpression(int minAge, int maxAge){ ParameterExpression parameter = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Person), "p"); Expression left = Expression.Property(parameter, "Age"); Expression minAgeCheck = Expression.GreaterThanOrEqual(left, Expression.Constant(minAge)); Expression maxAgeCheck = Expression.LessThanOrEqual(left, Expression.Constant(maxAge)); Expression combinedCheck = Expression.AndAlso(minAgeCheck, maxAgeCheck);
return Expression.Lambda<Func<Person, bool>>(combinedCheck, parameter);}
static void Main(string[] args){ // 使用 List<Person> people = new List<Person> { new Person { Name = "Alice", Age = 25 }, new Person { Name = "Bob", Age = 30 }, new Person { Name = "Charlie", Age = 35 }, new Person { Name = "David", Age = 40 } };
var ageRangeExpression = BuildAgeRangeExpression(28, 38); var filteredPeople = people.AsQueryable().Where(ageRangeExpression);
foreach (var person in filteredPeople) { Console.WriteLine($"{person.Name} - {person.Age}"); }}

總結
Func<T, TResult> 是一個通用委托,可以接受多個輸入參數并返回一個值。它非常靈活,適用于多種場景。
Predicate<T> 是Func的一個特例,專門用于返回布爾值的情況。它通常用于定義過濾條件。
Expression<T> 表示可編譯和執行的代碼塊。它允許在運行時檢查、修改和編譯代碼,特別適用于構建動態查詢和規則引擎。
這三種類型在C# .NET編程中扮演著重要角色,能夠幫助開發者編寫更加靈活、可重用和高效的代碼。根據具體的使用場景,選擇合適的類型可以大大提高代碼的表現力和可維護性。
該文章在 2024/11/7 10:27:20 編輯過